Electric Smelting Furnace(ESF)
Electric Smelting Furnace (ESF)
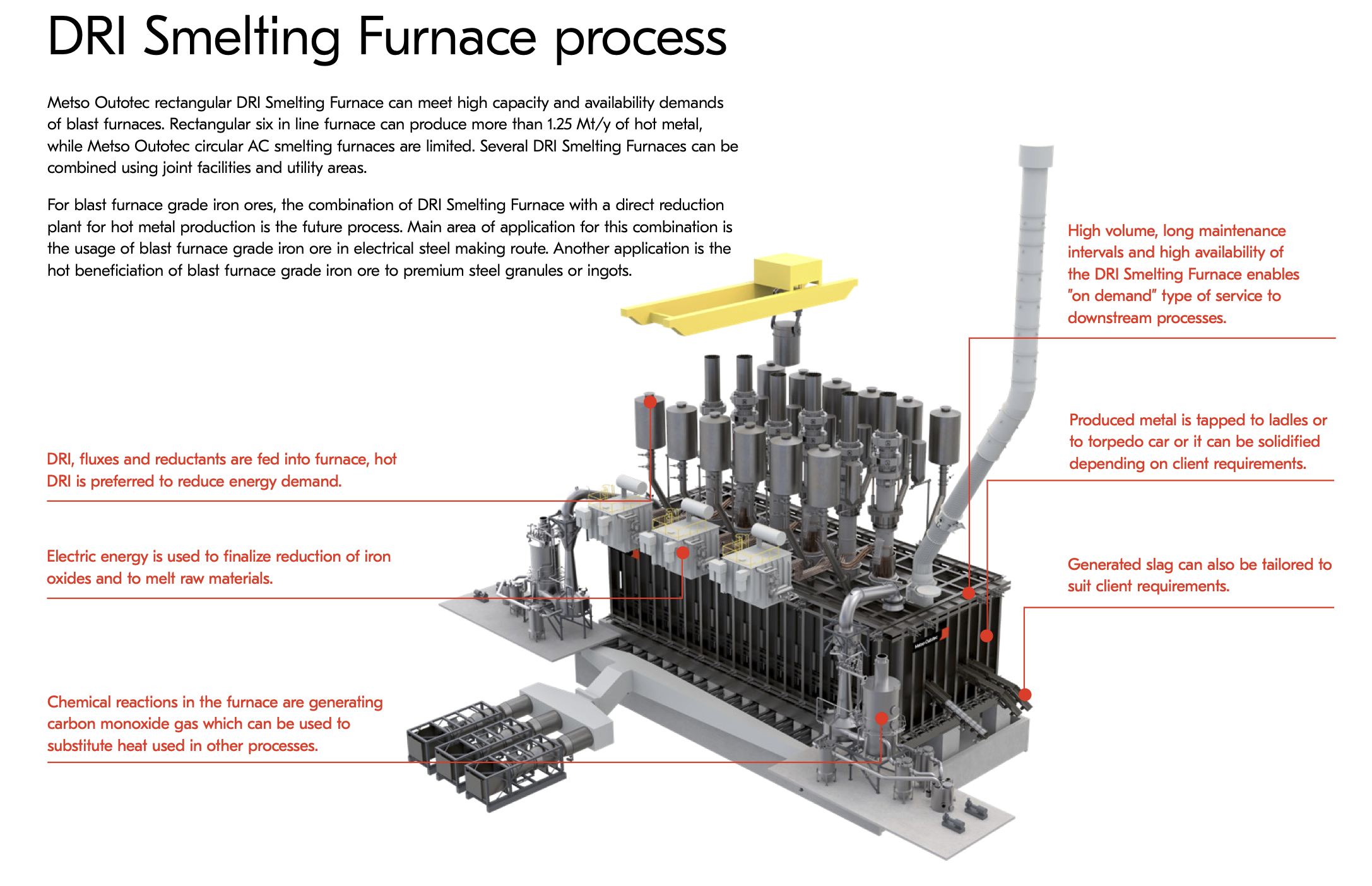
An Electric Smelting Furnace is designed to produce molten iron from direct reduced iron (DRI) or iron ore fines, often using hydrogen as a reducing agent.
A description from my reading, noting that I have no real understanding of what is involved is:
How an Electric Smelting Furnace Works
An Electric Smelting Furnace (ESF) is a high-temperature furnace used to melt Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) or iron ore to produce molten iron. Unlike traditional blast furnaces, ESFs do not require coke and can operate using renewable electricity, making them an important technology for low-emission or “green” iron production.
Step 1: Feed Preparation
The main input is Direct Reduced Iron (DRI), which is iron ore that has already had most of its oxygen removed. The DRI may be either cold (stored and transported) or hot (fed directly from a reduction unit to save energy).
Step 2: Charging the Furnace
The DRI is introduced into the furnace from the top or side. Sometimes, additional materials called fluxes (such as lime or dolomite) are added to help bind with and remove impurities during the smelting process.
Step 3: Electric Heating
Large graphite electrodes are lowered into the furnace, and a powerful electric current is passed through them. This generates intense heat, either through electric arcs or resistive heating, which melts the DRI inside the furnace.
Step 4: Melting and Reduction
As the furnace heats, the DRI melts into liquid iron. Any remaining iron oxide is further reduced—converted to pure iron—sometimes with help from carbon or residual gases in the furnace.
Step 5: Slag Formation
Impurities in the iron combine with the added fluxes to form a separate liquid layer called slag. This slag floats on top of the molten iron and is later removed or tapped off for disposal or reuse.
Step 6: Tapping the Molten Iron
Once the iron is fully melted, the furnace is tapped—usually through a hole near the base—and the molten iron flows into ladles or molds. It may be sent to another furnace, such as an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), for further refinement into steel.
Step 7: Gas Handling**
The smelting process produces gases like carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. These are captured and treated in exhaust systems. In some cases, the heat or energy in these gases is recovered and reused in the plant.
There are very few operating at scale globally