Electric Arc Furnaces
Electric Arc Furnace technology represents a highly efficient and flexible steelmaking process that utilizes electrical energy to melt scrap steel or direct reduced iron for steel production. This technology demonstrates particular advantages for recycling scrap metal and supports more sustainable steel manufacturing approaches compared to traditional blast furnace methods.
Core Technology and Process
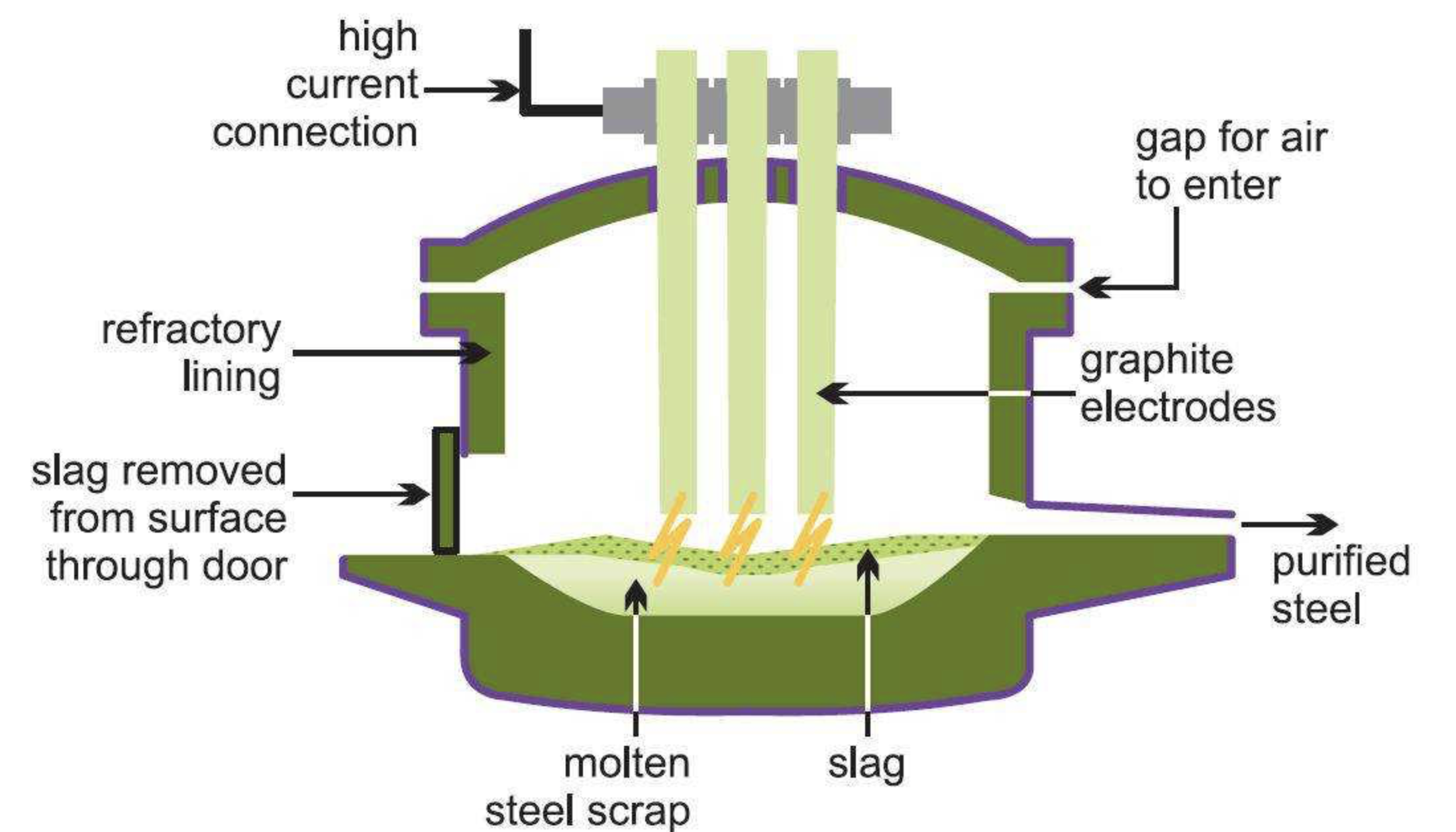
The Electric Arc Furnace operates through high-voltage electric arcs generated from graphite electrodes, creating intense heat reaching up to 3,500°C. The process typically utilizes scrap metal, DRI, or hot briquetted iron as primary feedstock materials. Production follows a structured four-stage approach beginning with charging scrap or DRI into the furnace, followed by melting through electric arc heat generation, refining through oxygen and carbon injections to remove impurities, and concluding with tapping molten steel into ladles for subsequent processing.
Environmental advantages include significantly lower CO₂ emissions compared to traditional blast furnaces, particularly when powered by renewable electricity sources. The technology offers superior flexibility in feedstock selection, rapid heat-up and shutdown capabilities, and a substantially smaller carbon footprint than conventional steelmaking processes.
Essential Components and Infrastructure
Modern Electric Arc Furnace systems incorporate several critical components that enable efficient operation. Graphite electrodes conduct electricity and generate the arcs necessary for metal melting. The furnace shell consists of a steel vessel with specialized refractory lining to withstand extreme temperatures. A swinging or liftable roof provides access for charging materials and electrode maintenance.
The tilting mechanism enables efficient tapping of steel and slag removal, while the oxygen and lance system supports refining processes and increases operational efficiency. A dedicated slag door facilitates slag removal operations. The transformer system steps down and regulates high voltage requirements for proper arc formation, ensuring consistent and controlled melting processes throughout production cycles.
Issues
Despite the advantages of Electric Arc Furnace technology, several operational and supply chain challenges affect performance and implementation across different markets and applications.
Scrap Quality Variability
Electric Arc Furnaces primarily depend on scrap steel as feedstock, but composition variations create significant operational complications. Inconsistent chemical composition results from fluctuating levels of elements like phosphorus and sulfur, directly affecting final steel quality specifications. Contaminants including non-metallic materials or undesirable metals complicate refining processes and require additional treatment steps. Residual elements such as copper and tin prove particularly problematic as they resist removal during standard refining procedures and can impair mechanical properties of finished steel products.
High-Quality Scrap Availability
The supply of clean, high-quality scrap steel remains constrained across global markets. Geographical disparities create situations where some regions maintain abundant scrap supplies while others experience significant shortages, affecting production planning and costs. Competition for quality scrap continues intensifying as green steel initiatives expand globally, driving up prices and creating supply security concerns for EAF operators.
Energy Consumption and Infrastructure Requirements
Electric Arc Furnaces demand substantial electrical energy inputs that create operational and economic challenges. High energy costs significantly impact operating expenses, particularly in regions with expensive electricity rates or limited renewable energy access. Infrastructure requirements include reliable and robust electrical systems capable of supporting EAF operations, necessitating substantial capital investment in power distribution and backup systems.
Environmental and Waste Management Concerns
While Electric Arc Furnaces demonstrate superior environmental performance compared to traditional blast furnaces, they generate operational challenges requiring careful management. Emissions including dust and other pollutants necessitate effective filtration and air quality control systems. Waste management responsibilities include proper handling and disposal of slag and other by-products, requiring specialized facilities and adherence to environmental regulations across different jurisdictions.
There has, as in so many other fields, been a strong learning rate in EAF energy consumption.
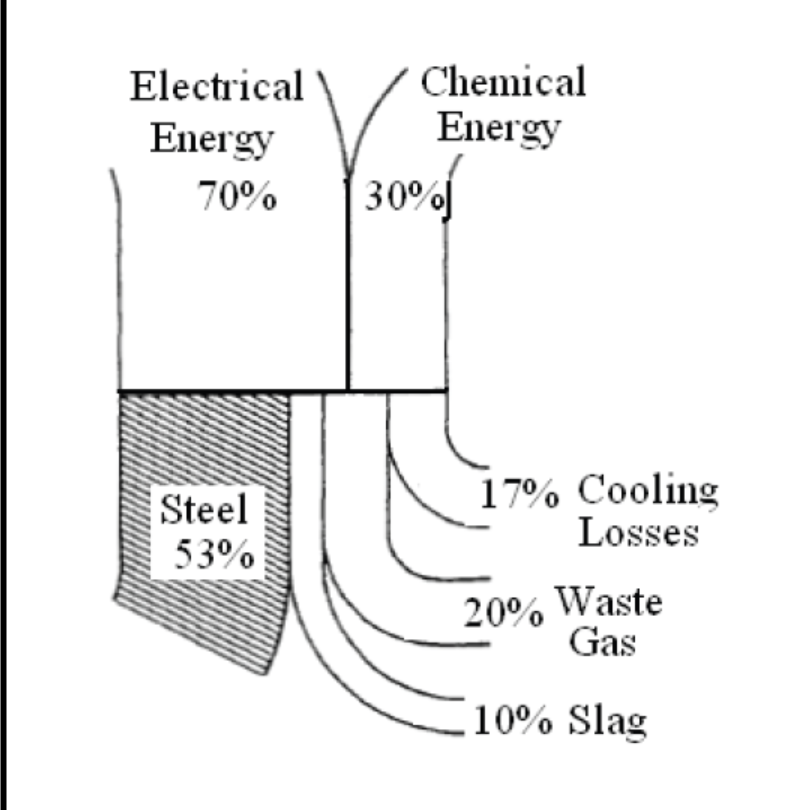
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF) are being greatly improved at a fast pace. Only 20–30 years ago today’s EAF performance would be impossible to imagine (Hurst, 1994). Owing to the impressive number of innovations the tap-to-tap time has been shortened to 30–40 min. for the best 100–130 ton furnaces operating with scrap. Accordingly, their hourly and annual productivity increased. Electrical energy consumption got reduced approximately in half, from 580–650 to 320–350 kWh/ton. Electrical energy share in overall energy consumption per heat dropped to 50%. Electrode consumption was reduced 4–5 times. Source: powerquality.blog
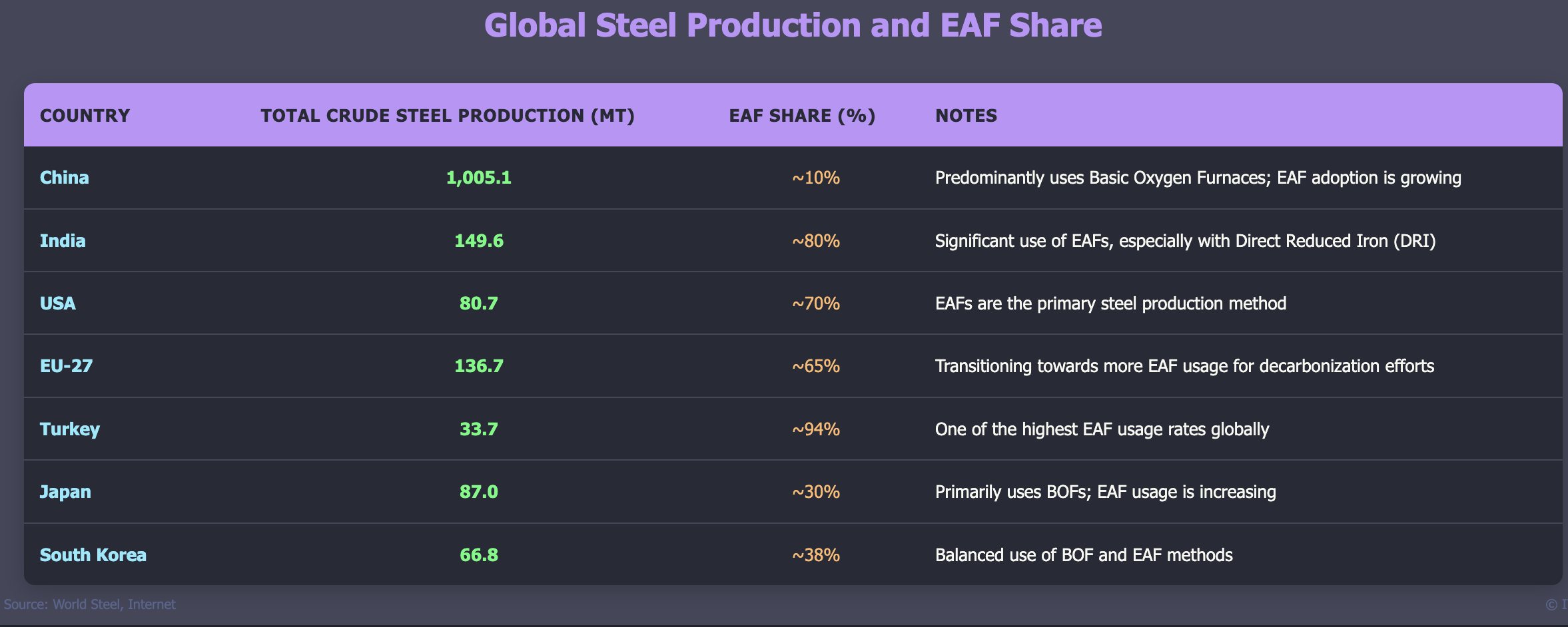
Global Steel Production and EAF Implementation by Country (2023)
Electric Arc Furnaces accounted for approximately 28.6% of global crude steel production in 2023, with significant regional variations reflecting different industrial strategies, resource availability, and environmental policies across major steel-producing nations.